What is Shockwave Therapy and How Can It Help You?
You may have heard that shockwave treatment is a safe and easy way to resolve chronic pain without surgery. If your doctor advises this rehabilitation modality, here is what to expect and what you should know.
What is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive medical treatment that uses the delivery of pulsating waves to damaged or injured ligaments, bones, tendons, and fascia to promote the body’s natural self-healing process.
Shockwave therapy is also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT). Because of its effectiveness to treat pain, shockwave physio is usually recommended as a first-line treatment for overuse disorders.
How Does Shockwave Therapy Work?
ESWT works by sending transient waves that enter deep into the cellular level of the scarring tissue where they propagate three-dimensional pressure. Shockwave has a positive phase, which applies mechanical force to the affected area, and a negative phase, which applies cavitation producing gas bubbles that further create and expand waves.
Mechanical pressure increases the cell permeability, microscopic circulation, and metabolism of the treated tissue. Consequently, healing happens faster. If the area has calcified deposits, the smaller waves created from the negative phase cavitation can create additional impact and dissolve them.
Shockwave therapy stimulates the growth of fibroblastic cells found in soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, muscles and connective tissue. It promotes the creation of osteoblastic (bone-forming) cells, responsible for new bone tissue and healing bone injuries.
ESWT for Pain Relief
Pain reduction as a result of ESWT happens in two ways:
- Short-term pain reduction mechanism called hyperstimulation anaesthesia overstimulates local nerve endings, thus reducing their sensitivity.
- Long-term pain reduction mechanisms called gate-control mechanisms stimulate local nerve endings to the degree that recalibrates pain by alternating perception.
Despite the similarities, shockwave therapy has unique physical characteristics, making them different from standard ultrasound therapy.
Shockwave (SWT) vs. Ultrasound (UT)
Although the mechanism by which they help patients is not identical, both treatments can be used for treating the same disorders. Ultrasound waves resemble the ripple effect of a small rock thrown into the water, while shockwaves resemble the V-shaped bow wave created by boat movement.
UT can produce thermal on non-thermal effects depending on the frequency, intensity, and duration of the treatment. Electric signals sent to the inside of the body raise the temperature promoting blood circulation and faster healing. UT also stimulates tissue recovery on a molecular level by boosting protein synthesis.
SWT is more focused on healing by re-injuring and inhibiting the transmission of pain stimuli.
Benefits of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
Observed effects of shockwave therapy include:
- Formation of new blood vessels at the tendon-bone junction
- Proliferation of tenocytes (ligament and tendon cells)
- Differentiation of bone stem cells
- Increased infiltration of white blood cells
- Stimulation of growth factor and protein synthesis
The initial application of shockwave therapy was for treating urinary stones. After expanding from urology to orthopaedics, this modality has proven to be effective for treating a range of musculoskeletal and soft tissue disorders, including fracture healing.
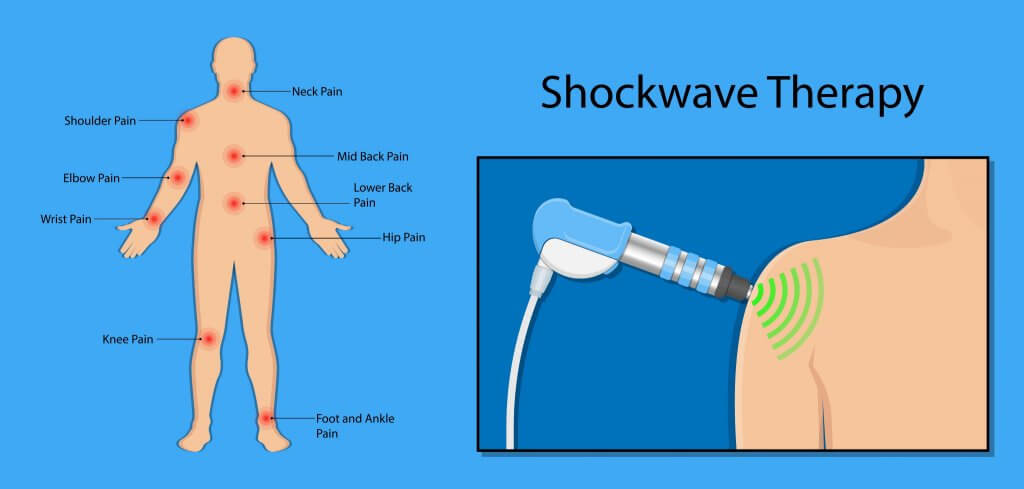
Shockwave Treatment Indications
Shockwave therapy is typically applied to chronic conditions that affect larger tendons and their bone insertions, such as tendinopathies and fasciopathies. Then list of specific indications extends to:
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendinopathy
- Hamstring tendinopathy
- Ankle bursitis
- Tennis elbow
- Golfer’s elbow
- Calcific tendonitis
- Patellar tendinosis (Jumper’s knee)
When the patient doesn’t respond well to other physiotherapy treatments, for example, rest and painkillers, shockwave therapy is recommended as a method to build up the biomechanics of the affected area, strengthen the tissue, and improve load tolerance. A series of shockwave treatments can successfully produce health improvements and increased mobility in the majority of the cases. Most people respond well to the therapy and are happy with the achieved results.
You may notice a slight improvement after the first treatment, but it usually takes several for optimum results. Each treatment takes up to 30 minutes. For patients who don’t feel improvement after three sessions, further investigations should be done to assess why the patient is not improving.
What to Do and not to Do after Your Treatment
Avoid doing any strenuous activity that affects the treated area for 24 hours after the shockwave session even when not in pain. The healing mechanism of the treatment instigates an anti-inflammatory response which goes away after a day. Therefore, skip anti-inflammatory medications and ice application.
When not to Use Shockwave Therapy
ESWT is relatively safe to use unless you have some of the following contraindications:
- Pregnancy
- Undergoing cancer treatment
- Implanted cardiac pacemaker
- Within 90 days of a corticosteroid injection treatment
- Blood clot disorder
- Patient is on anticoagulants (blood thinning medication)
Shockwave therapy is tolerated well by patients with only a small number experiencing discomfort that could be managed by the physiotherapist during the treatment. If you experience an adverse effect, the treatment will be adjusted to best suit your needs.
Types of ESW Therapy
The different types of devices used for shockwave therapy are based on three physics mechanisms:
- Electromagnetic
- Piezoelectric
- Electrohydraulic
Physiotherapy clinics use radial and focused shockwave therapy to treat different disorders. You will be advised to undergo the most suitable treatment by your doctor.
How Can Shockwave Help You
Confirmed benefits from ESWT treatment include:
- Improved circulation and oxygenation of the treated area to accelerate healing
- Increased number of mast cells that are critical for wound healing and protection from pathogens
- Generation of more collagen for firmer tissue structure
- Breaking down calcium build-up that is excreted by the lymphatic system from areas suffering from microtrauma
- Reduced pain from lowered substance P Levels.
Shockwave therapy is a versatile treatment that successfully treats several chronic conditions and is effective when used individually or in combination with other treatments. It produces long-lasting effects for patients suffering from problems with the fascia in the limbs, who have reported they experienced no pain up to six months after treatment.